Appearance
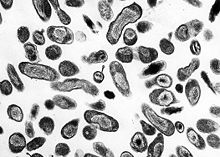
C. burnetii, the Q fever causing agent
The pathogenic agent is to be found everywhere except New Zealand.The bacterium is extremely sustainable and virulent: a single organism is able to cause an infection. The common way of infection is inhalation of contaminated dust, contact with contaminated milk, meat, wool and particularly birthing products. Ticks can transfer the pathogenic agent to other animals. Transfer between humans seems extremely rare and has so far been described in very few cases.
Some studies have shown more men to be affected than women, which may be attributed to different employment rates in typical professions.
"At risk" occupations include, but are not limited to:
Some studies have shown more men to be affected than women, which may be attributed to different employment rates in typical professions.
"At risk" occupations include, but are not limited to:
- veterinary personnel
- stockyard workers
- farmers
- shearers
- animal transporters
- laboratory workers handling potentially infected veterinary samples or visiting abattoirs
- people who cull and process kangaroos
- hide workers.
